Wednesday, March 22, 2006
M&b Wedding Dance Giude
MECHANISMS OF TRANSFORMATION OF MOTION
processing mechanisms in straight circular motion .
1.- Sistema piñón-cremallera.
Es un piñón o rueda dentada de dientes rectos, engarzado a una cremallera, se desplaza con movimiento rectilíneo.
Este mecanismo permite transformar el movimiento rectilíneo en un movimiento circular, es un mecanismo reversible. Se utiliza en sacacorchos, etc.
2.- Sistema tornillo-tuerca.
Consta de un tornillo y de una tuerca (como su propio nombre indica), cuyo diámetro coincide con el del tornillo. Si el tornillo turning the nut moves with a linear motion, provided that the orientation remains fixed, and vice versa. It is used in screw caps, etc.
3 .- Joint-winch handle.
A handle is a bar that is attached to a shaft that spins. The force required to rotate is less than it would have to apply directly. The mechanism is the lathe, which consists of a drum that rotates around its axis in order to drag an object.
A lathe is in equilibrium when it meets this equation:
F × f = R * R
F = R * R / d
equalities in "F is the force applied.
-f: is the radius of the crank.
-R: the resistance.
-r: is the radius of the lathe.
Ryd If the ratio is small enough, the winch will lift weights with little effort.
Transformation mechanisms of circular motion in straight alternative.
1 .- rod-crank assembly.
is formed (as the name suggests) with a handle and a bar called crank. Is articulated at one end to said crank and the other with an element describing a reciprocating motion.
rotate the wheel, crank transmits the circular movement of the rod. This system also works in reverse. It is used in machine tools, etc..
Examples of application of the rod-crank mechanism
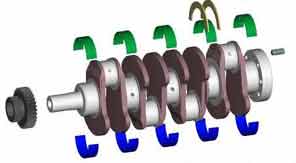
* crankshaft.
Placing a series of cranks on the same axle, each axle elbows acts as a crank, and crank set is called.
The crankshaft transforms the rotation movement of step alternative movements of rods. You can also convert reciprocating push rods in a rotational movement.
This mechanism is used in combustion engines, sewing machines, etc.
Examples combustion engine crankshaft
Máquina de coser
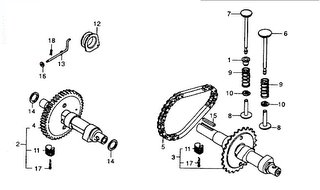
2.- Leva y excéntrica.
La leva es, una rueda con un saliente que empuja un seguidor a su paso. Se pueden añadir más salientes e introducir perfiles más o menos abruptos para conseguir movimientos más complejos.
De este modo, la leva transforma el movimiento de rotación de la rueda en un movimiento lineal del seguidor o varilla, que recorre el perfil de la leva cuando esta gira.
Un conjunto de levas colocadas sobre el mismo eje se denomina árbol de levas.
La excéntrica consiste en una rueda cuyo eje de giro no coincide con el centro de la circunferencia. Transforma el movimiento de rotación wheel in a reciprocating linear movement of the rod.
Camshaft
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)





0 comments:
Post a Comment